
Holiday in Duckburg (1989), painting by Carl Barks.
The Duck universe (also called the Donald Duck universe or Scrooge McDuck universe) is a fictional universe where Disney cartoon characters Donald Duck and Scrooge McDuck live. It is a spin-off of the older Mickey Mouse universe, yet has become much more extensive. "Duck universe" is a term used by fans and is not an official part of the Disney lexicon.
The world's continuity has been primarily built in comics by the late Carl Barks, but has its roots in the Donald Duck short film series and the Silly Symphony comic strip by Ted Osborne and Al Taliaferro. Other cartoonists have built on Barks' work including Don Rosa and the late Romano Scarpa. Other media includes children's books, such as Little Golden Books and Little Big Books, television series, such as DuckTales (1987-1990) and Darkwing Duck (1991-1992), and video games, such as QuackShot (1991) and Goin' Quackers (2000).
Life in the Duck universe centers around the city of Duckburg in the fictional U.S. state of Calisota. The world is also a parallel universe and characters sometimes visit real-world locations and meet historical figures.
History[]
Most of the characters have appeared in the 1980s Disney cartoon series DuckTales. Disney's Darkwing Duck series is nominally set in the DuckTales universe, in a metropolis called St. Canard, although aside from sharing the denizen Launchpad McQuack, and a few crossover episodes involving GizmoDuck, there is no interaction. The Darkwing Duck material doesn't appear in Barks' comics, as the Darkwing Duck TV series was created decades after Barks' active years as a comic artist. Later, a few characters would be the main characters in the show Quack Pack.
However, in the magazine Disney Adventures, there was a five-part crossover/storyline titled "Legend of the Chaos God" which began with TaleSpin, and continued with Chip 'n Dale Rescue Rangers, Goof Troop, and DuckTales, then concluded with Darkwing Duck.
Duckburg was the setting of the 1987 animated series DuckTales. The cartoon's version of Duckburg was based heavily on the comics' version. Duckburg appeared in the 1990s animated series Quack Pack. In Quack Pack, Duckburg was populated almost entirely by human beings, with Donald, Daisy, and their nephews as the only anthropomorphized animals that usually appeared. Moreover, the Money Bin is nowhere to be seen. Duckburg was the setting for one of the three initial levels of the video game Quackshot and also for the second level of the video game Donald Duck: Goin' Quackers.
Duckburg was also used for the setting of Mickey's Birthdayland (later Mickey's Starland) at Walt Disney World's Magic Kingdom from 1988 to 1996. It even included Grandma Duck's Farm and a statue of Cornelius Coot, though it was more of a rural town than a burgeoning metropolis. The connection to Duckburg was removed as the land was renovated in 1996 to become Mickey's Toontown Fair. However, the Cornelius Coot statue remains.
Duckburg[]

Duckburg, as seen in the animated series DuckTales.
Duckburg is the fictional city that serves as the home of Donald Duck, Scrooge McDuck, Huey, Dewey, and Louie, Daisy Duck, and most of their supporting cast. Duckburg was first mentioned in Walt Disney's Comics and Stories #49 in 1944, and was created by Carl Barks.
Duckburg is described as a medium size city located in the fictional U.S. state of Calisota. In comic writer Don Rosa's stories, Duckburg is located on the west coast of the United States, though other writers often leave the city's location more vaguely defined. However, in Don Rosa's The Life and Times of Scrooge McDuck, the author alludes to where exactly he has situated Duckburg: "I won't bother to say precisely where I situated Duckburg and Calisota on America's west coast... but if you get out a good map and compare the coastline, you'll see that I stuck the old gold-prospector's adopted hometown directly across the bay from a very appropriately named actual city."
In the DuckTales episode "Double-O-Duck", a map is shown which shows Duckburg as being located somewhere in Virginia or North Carolina. The city is populated by various anthropomorphized animals, with ducks, dogs, and pigs the most dominant ones. The population is estimated 316,000.
The most prominent landmark in Duckburg is Scrooge McDuck's Money Bin, a giant building sitting on Killmotor Hill (formerly known as Killmule Hill) in the center of town. The Money Bin contains both office space and, most famously, three cubic acres of money, the results of Scrooge's lifetime of business and treasure-seeking adventures. Another major landmark in some stories is a large statue of Duckburg's founder, Cornelius Coot.
Duckburg is a major center for Space exploration. Expeditions have been launched from Duckburg to the Moon, Mars, Venus, the Asteroids, and more remote parts of the Galaxy. The town also features a sea port and is in proximity to several mountains, the most notable being "Old Demon Tooth", usually depicted as a towering pointed peak leaning extremely to the side.
Duckburg is home to Yarvard University (a play on the universities of Harvard and Yale), an institution more notable for its athletic teams than for its academic achievements.
Located near Duckburg is a Farm owned and run by Grandma Duck, a direct descendant of Cornelius Coot and Donald's paternal grandmother. Donald's cousin Gus Goose also lives on Grandma's farm as a "farmhand". The farm is often a gathering site for various Duck family holiday celebrations.
In other languages, Duckburg (for example Entenhausen in German) is not only home of "the Ducks", Mickey Mouse and friends live there too.
History[]
In the comics, the location that would eventually become known as Duckburg was originally known as "Fort Drake Borough", a fort built in the 16th century by British explorer Sir Francis Drake. By the 19th century, the fort had been handed over by its departing British occupants to Cornelius Coot, who renamed the fort "Duckburg". "Drake" means a male duck, while "borough" and "burg" are synonyms.
Duckburg remained a quiet, small town up until the arrival of wealthy businessman Scrooge McDuck. McDuck bought the old fort from Clinton Coot, a descendant of Cornelius. Scrooge proceeded to construct his famous Money Bin and established various businesses in and around Duckburg. This construction caused Duckburg's population to swell and turned the small town into a bustling city within several decades' time.
Duckburg is the largest city in the state of Calisota, but not the capital city. There are no references to the governor, legislature, Capitol, etc., of Calisota in any of the many stories about Duckburg. Duckburg seems to have its own governor, however, if it is not a sort of city state. In more than one story a "Duckburg embassy" is shown, which would place it outside the USA at a legislative level. In a story by Barks the Duckburg embassy displays a flag of Duckburg, which consists of a white duck over a green field. However, in the Don Rosa story "His Majesty, McDuck" (Uncle Scrooge Adventures #14, Gladstone Aug. 1989) Scrooge gains a short-lived independence from the United States for Killmotor Hill, thus placing Duckburg within the U.S.
Duckburg maintains a traditional rivalry with Goosetown, another city of Calisota.
Fort Duckburg[]
Fort Duckburg is a fictional place in the fictional state of Calisota. It was originally created by Carl Barks and then intensively developed by Keno Don Rosa. It was, in the fictional universe of Barks and Rosa, first built by Sir Francis Drake, who named it "Fort Drakeborough". It was later acquired by Cornelius Coot, who changed the name from "Drakeborough" to "Duckburg" (same meaning). Clinton Coot, the son of Cornelius, sold it to Scrooge McDuck, who built his world-famous Money Bin in its site. This would eventually cause McDuck an incredible variety of problems and dilemmas. The first one was caused by the Junior Woodchucks, who were squatting in the site and using it as their headquarters, even though they didn't have legal title to it. The dispute led to a small war.
Calisota[]

The map shown on the left indicates the location of Duckburg ["Donaldville"] in Calisota [in French]. The Calisota map resembles a map of Northern California (right), with Duckburg corresponding to a coastal area in Humboldt County near the city of Eureka, located on Humboldt Bay.
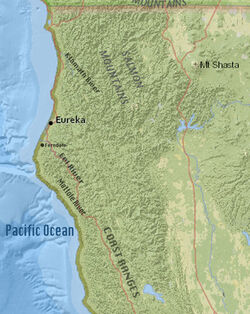
The map shown on the left indicates the location of Duckburg ["Donaldville"] in Calisota [in French]. The Calisota map resembles a map of Northern California (right), with Duckburg corresponding to a coastal area in Humboldt County near the city of Eureka, located on Humboldt Bay.
The map shown on the right indicates the location of Duckburg ("Donaldville") in Calisota.
Calisota is a fictional U.S. state, created by Carl Barks in his story "The Gilded Man" (Four Color #422). Duckburg is among the cities located there, as well as Goosetown and Mouseton.
Although it has many fictional elements and a variable climate, Calisota is probably roughly equivalent to Northern California. Duckburg is located north of Los Angeles and San Francisco, with a map in Don Rosa's The Life and Times of Scrooge McDuck showing Calisota corresponding to the part of California north of Sacramento. Its location roughly corresponds to the borders of the real-world proposed state of Jefferson.
The name is a blend of California and Minnesota, supposedly to allow all kinds of weather or climate in the stories, although Calisota bears very little in common with the latter (a state in the Upper Midwest, far from the ocean coasts and Northern California region weather is sufficiently variable by itself). The name also be a reference to Calistoga, a small town in Napa County, which, like Duckburg, is north of San Francisco.
Money Bin[]
The Money Bin is the building where Scrooge McDuck stores the portions of his money he earned by himself. Carl Barks invented the "money swim" in 1950, followed by the "Money Bin" in 1951.
The Money Bin was built in 1902, shortly after Scrooge entered the diamond market and could no longer sleep at night because all the money he was storing under his mattress raised his bed too close to the ceiling, necessitating a more suitable storage facility for his money. His favorite pastime is to dive off a springboard into his money and swim through it.
Don Rosa has said that Scrooge had earned all the money in his bin by himself, but not only does the bin's size possibly contradict this idea, in Rosa's Life and Times of Scrooge McDuck, he said that Scrooge was traveling around the world, starting businesses and having the money sent home. It is unlikely that Scrooge actually earned that money just when he started the business. In the same series, however, he states that he doesn't keep all his money in his bin. Also, in Rosa's Last Sled to Dawson, he implied that Scrooge McDuck no longer earns money with his "own two hands".
Although the Money Bin is a twelve-story skyscraper and vault (filled with "three cubic acres" of money). On various occasions, it has been pulled around by a tractor, lifted to the top of a mountain, stolen by aliens from the bottom of the ocean, and blasted open with a cannon. The traditional location of the Money Bin is on top of Killmotor Hill. The Money Bin sits atop Futterman's Fault, a fault line which would prove catastrophic in the event of an earthquake (this earthquake occurred in the story Land Beneath the Ground!).
The Money Bin is the victim of repeated assaults by Scrooge's enemies who try to steal his money, such as the Beagle Boys, who are after the bulk of Scrooge's money, and Magica DeSpell, who is after Scrooge's "Number One Dime" (the first dime Scrooge ever earned). To protect against these attempted break-ins, Scrooge has installed the greatest security system in the world to thwart any thought of even trying to intrude onto the premises.
Barks defined the volume of money contained inside as "three cubic acres", but the exact meaning, and therefore the volume, of a "cubic acre" is subject to interpretation by the reader, since an acre is a measure of area, not length, a cubic acre would be a 6-dimensional space of 247,961,850,048,000 feet to the sixth power. A series of blueprints created for the Scrooge McDuck story The Beagle Boys vs. the Money Bin by Don Rosa state that the money bin is approximately 127ft tall, and 120ft wide. In the story, said blueprints are accredited to an architect named Keno D. Rosa (which is Don Rosa's actual name).
The Norwegian name for the Money Bin is "Pengebingen" and has become regular word in the Norwegian language for a large amount of money or cash.
Russell W. Belk mentions that the Money Bin in Material Values in the Comics: A Content Analysis of Comic Books Featuring Themes of Wealth, where he remarks that Scrooge's "childish fascination with money", where he takes pleasure in diving and swimming in the Money Bin, might account for Scrooge not being portrayed as a villain. Penelope Fritzer in the article Scrooge McDuck: Postmodern Robber Baron considers it possible for the Money Bin to symbolize the entire Disney empire.
Glomgold's bin[]
Flintheart Glomgold also owns a Money Bin, located near Limpopo Valley. Glomgold's bin substitutes the dollar sign ($) that appears on Scrooge's with a pound sign (£). This is due to Glomgold's heritage which puts him in as a citizen of South Africa with British blood compared to Scrooge who embraced America despite his pure Scottish blood. It has been said that Glomgold's bin is protected by the native African wildlife.
Number One Dime[]
- Main article: Number One Dime
The Junior Woodchucks[]
- Main article: Junior Woodchucks
The Junior Woodchucks are the Scouting organization to which Huey, Dewey, and Louie belong. They have a uniform with a coonskin cap. The Junior Woodchucks were created by Carl Barks in 1951, in the story "Operation St. Bernhard" (Walt Disney's Comics and Stories #125). Later stories introduced a similar organization for girls, Junior Chickadees, to which Daisy Duck's nieces, April, May, and June belong. A hallmark of the Woodchucks are exalted titles and ranks (Huey, Dewey, and Louie being promoted to become Ten Star Generals in the 1952 story of that name) and the awarding of buckets of badges, along with severe ideals as to decorum. In this way, Barks poked gentle but pointed satire at aspects of the Boy Scouts.
Brutopia[]
Brutopia (a portmanteau word from brute and Utopia) is a fictional country appearing in several Donald Duck stories. It was created by Carl Barks in 1957. Brutopia is a hostile country, aiming for world domination. It is clearly a caricature of the Soviet Union. In the Duck universe, Brutopia occasionally attempts to steal Scrooge's money so as to devastate the American economy and to fund the creation of doomsday weaponry. The currency of Brutopia is the peso. Its coat of arms is the hammer and handcuffs.
Whether Brutopia is a stand-in for all of the former USSR or just for part of it, varies with the story. Sometimes parallels to Russia are drawn directly. Don Rosa has suggested that Brutopia might instead represent the eastern part of Siberia.
The language of Brutopia often looks somewhat Slavic. On some occasions, it is written in Cyrillic script. On the other hand, Brutopians seem to speak perfect, non-accented English; and other stories show English language texts being used by Brutopians, suggesting that the national language could be English.
In 1957, Brutopia's military spending budget amounted to one trillion dollars plus all the kitchen sinks of its happy people (a number that on closer inspection turned out to be five). Scrooge McDuck outbid the Brutopian government by paying one trillion dollars and six kitchen sinks for a sample of the recently discovered substance of bombastium.
According to Disney stories written and drawn in the post-Barks period, the capital of Brutopia is Brutengrad. The country is no longer a dictatorship, as the former regime was overthrown by a popular revolt, and the tyrant forced to flee.
In modern usage[]
The Australian center-left then Opposition Leader, Kevin Rudd, used the term to criticize the economic policies of the Howard Government, notably in an essay in the November 2006 issue of The Monthly magazine entitled "Howard's Brutopia: The Battle of Ideas in Australian Politics". According to Rudd, a "brutopia" is a place of "unchecked market forces", incompatible with both "fairness" and "the so-called conservative institutions of family, community, church and country". Rudd argues that Australia is becoming such a place due to the Howard Government's "market fundamentalism". For example, he claims that as a result of the Government's labour market liberalization, "Breadwinners are now at risk of working less predictable shifts, spread over a seven-day week, not sensitive to weekends and possibly for less take-home pay. The pressures on relationships, parenting and the cost and quality of childcare are without precedent... Neo-liberalism's core philosophical dilemma is that it has no answer to the relentless march of market fundamentalism into the sanctum of the family itself. The Christian churches should be concerned about where this march ultimately ends." In the essay, Rudd writes that the term "brutopia" was borrowed from British conservative Michael Oakeshott.
The then Australian Treasurer, Peter Costello, ridiculed Rudd's use of the term on 8 February 2007 in the Australian Parliament: "We have unemployment at 4.5 per cent. We have had 300,000 new jobs in the last year and we have had 2 million new jobs over the last 10 years. The Leader of the Opposition says that all of this represents free market fundamentalism, and he describes this economy as Howard's Brutopia... There has been some speculation as to what a Brutopia is. I can now authoritatively inform the House that Brutopia is a fictional country which appears in several Donald Duck stories... Labor [is] drawing inspiration for its economic analysis from a Donald Duck magazine, Mr Speaker! This is the evolutionary cycle of the Labor Party. We have now moved from Mark Latham's roosters to Kevin Rudd's ducks, Mr Speaker. Managing the Australian economy, which is a $1 trillion economy, takes experience and commitment—and you do not get your analysis from Donald Duck comics. It is much more serious than that."
Bombastium[]
Bombastium is a fictional chemical element. Its Atomic number and atomic symbol are unknown. Bombastium is stated to be the rarest element in the world. Even though it is very coveted, its usage potential is entirely unknown. One characteristic is that it tastes different every time you try it, and scientists eventually discovered that one atom of bombastium dropped into a barrel of water becomes one barrel of ice cream - a different flavor of ice cream each time. To avoid evaporation, bombastium must be kept frozen.
The last piece of bombastium known to exist (about the size of a soccer ball) was acquired by Scrooge McDuck of Duckburg in 1957, but at that time it was also heavily sought after by the hostile nation of Brutopia. Brutopia's military spending budget that year amounted to one trillion dollars plus all the kitchen sinks of its happy people. Scrooge McDuck therefore had to pay one trillion dollars plus six kitchen sinks to win the auction.
The element was also used for the 5-part DuckTales episode Time is Money, which introduced Bubba the Cave Duck. In this cartoon episode, bombastium is the fuel for one of Gyro Gearloose's inventions, a time traveling helicopter named the Millennium Shortcut. The bombastium itself must be kept frozen in order for it to be usable as fuel (a small freezer is equipped onboard the Shortcut for this purpose). Otherwise, the Shortcut couldn't travel through time.
One of the treasures that can be obtained in the computer game DuckTales: The Quest for Gold is bombastium. Unlike the other treasures, bombastium is worth more than just money, as Gyro Gearloose can use it to build a matter transporter which takes away the risk of flying from place to place while having the possible downside of sending the player to a location they hadn't intended to go.
See also[]
External links[]
- A history of Duckburg, based on Barks' and Rosa's stories
- A study of Duckburg's location plus various Duckburg maps
 Duck universe at INDUCKS
Duck universe at INDUCKS- The Junior Woodchuck Guidebook
- The Money Bin Who's who in Duckburg
- Who's Who in Duckburg - Brutopia
| This page uses content from the English Wikipedia page Duck universe. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. Text from Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. |
