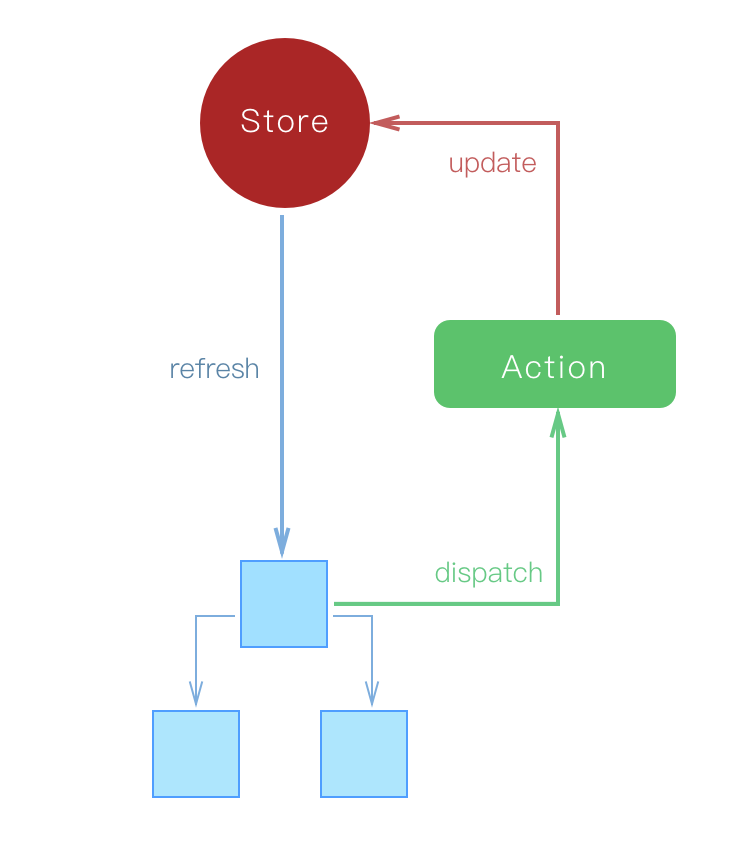
San 框架的官方应用状态管理套件,其理念是类似 flux 的单向流。
虽然应用状态管理已经是流行的理念,我们依然推荐您在开始之前,先看看 为什么要进行应用状态管理,可能会有些思考和启发。
提示:使用 san-store 需要同时使用 san-update 2.x 创建状态变更器,san-store 将使用此变更器更新 store 中的应用状态。
NPM:
$ npm i --save san-store san-update
import {store, connect} from 'san-store';
import {builder} from 'san-update';
store.addAction('changeUserName', function (name) {
return builder().set('user.name', name);
});
let UserNameEditor = connect({
name: 'user.name'
})(san.defineComponent({
submit() {
store.dispatch('changeUserName', this.data.get('name'));
}
}));从例子开始和模仿比死啃枯燥的文档要更人性化。 Todos项目 和 RealWorld App 展示了如何在项目里使用 san-store 进行状态管理。 多store的Todos项目 展示了如何再项目中使用 多 store connect 及 composition api 的用法。
本文档描述了 san-store 的基本使用场景。想了解 san-store 都提供了什么,可以参阅 API文档
一个应用具有唯一的应用状态源,在一个地方管理整个应用的所有状态,是一个比较共识的方式。所以 san-store 提供了默认的 Store 实例。绝大多数时候,应用开发者不需要手工创建自己的 Store 实例,只需要 import 默认的 store。
import {store} from 'san-store';
// 通过 getState 方法,获取 store 中的状态数据。
console.log(store.getState('user.name'));store 并没有提供修改状态数据的方法,修改状态数据只能通过 dispatch action 来做到,具体细节请参考 Action 章节。通过 addAction 方法可以添加 action。
store.addAction('changeUserName', name => builder().set('user.name', name));当同一系统中有不同团队开发自己的业务模块,各团队之间没有状态共享,可以考虑分别建立 Store 实例进行开发。通过 new Store 创建自己的 Store 实例。创建时可以传入初始化数据和声明 actions。
import {Store} from 'san-store';
import {builder} from 'san-update';
let myStore = new Store({
initData: {
user: {
name: 'your name'
}
},
actions: {
changeUserName(name) {
return builder().set('user.name', name);
}
}
});本节最后,还是要强调下,应用开发应当遵循 一个应用具有唯一的应用状态源。说白了就是 要按常理出牌。
通过 addAction 方法可以为 Store 添加 Action。 Action 是 san-store 最重要的组成部分之一,它:
- 是一个函数
- 在一个 store 内每个 action 具有唯一名称,通过名称 dispatch
- 是 store 更新状态的唯一入口
- 状态更新是同步的,这使得状态更新可依赖当前状态环境,可被记录、被追溯和重放
如果你使用了 san-store,Action 应该是你业务组件的唯一出口:用户操作事件等需要改变应用状态时,都应该 dispatch Action。
Action 接收一个 payload,返回一个 san-update 的 builder 对象。store 使用 builder 对象生成状态变更函数,并执行它,使 store 内部的状态得到更新。当然,如果当前 action 不期望对 store 的状态进行更新,可以不返回 builder 对象。
import {builder} from 'san-update';
store.addAction('changeUserName', function (name) {
return builder().set('user.name', name);
});
// 通过名称 dispatch
store.dispatch('changeUserName', 'erik');san-update 是一个 Immutable 的更新对象库,其提供了一些更新函数(如set、push等),通过 newObj = set(oldObj, 'x', 1) 的使用形式让对象更新 Immutable。builder 是 san-update 提供的一个很好用的功能,通过 builder 你可以预定义一系列的数据更新操作,然后通过 builder.build 方法可以获得一个更新函数。san-store 就是利用这个功能,使用 action 返回的 builder 生成对象更新函数,再调用它进行 store 内部状态更新。
san-update 的 builder 支持预定义所有 san-update 支持的数据操作,通过 san-update文档:可用指令 可以���看所有操作类型。常用的有:
- apply: 对现有数据项应用更新
- set: 设置数据项
- remove: 数组移除项
- push: 数组push操作
- pop: 数组pop操作
- unshift: 数组unshift操作
- shift: 数组shift操作
- splice: 数组splice操作
使用前请阅读 san-update文档:使用builder构建更新函数 进行详细了解。
Action 的第二个参数是一个对象,其中的 getState 方法可以用于获得当前 store 中的应用状态。这个方法是 this 无关的。
import {builder} from 'san-update';
store.addAction('initCount', function (count, {getState}) {
if (getState('count') == null) {
return builder().set('count', count);
}
});
store.dispatch('initCount', 10);如果我们的更新操作仅依赖于当前数据状态项的值,也可以使用 san-update 提供的 apply 方法。
import {builder} from 'san-update';
store.addAction('initCount', function (count) {
// apply 意思是:在原有的值上应用新的值
return builder().apply('count', oldValue => {
return oldValue == null ? count : oldValue;
});
});
store.dispatch('initCount', 10);同步的 Action 返回一个 builder,并立即更新数据状态,但我们经常会遇到异步的场景,常见的比如请求数据、返回并更新应用状态。Action 在设计上作为 业务组件的唯一出口, 对异步支持的方式如下:
- 返回一个 Promise 时,当前 Action 为异步
- 返回一个 builder 或什么都不返回时,当前 Action 为同步
下面是一个简单的例子: 一个列表请求的行为,此时要显示 loading,在请求返回时更新应用状态中的列表项,同时隐藏 loading。
import {builder} from 'san-update';
store.addAction('fetchList', function (page, {getState, dispatch}) {
dispatch('showLoading');
dispatch('updateCurrentPage', page);
return requestList(page).then(list => {
if (getState('currentPage') === page) {
dispatch('updateList', list);
dispatch('hideLoading');
}
});
});
store.addAction('showLoading', function () {
return builder().set('loading', true);
});
store.addAction('hideLoading', function () {
return builder().set('loading', false);
});
store.addAction('updateCurrentPage', function (page) {
return builder().set('currentPage', page);
});
store.addAction('updateList', function (list) {
return builder().set('list', list);
});
// 这里模拟一下,意思意思
function requestList(page) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
let pageList = [1, 2, 3];
resolve(pageList);
}, 500);
});
}例子中有下面几个要点:
- 异步 Action 可以多次 dispatch 其他的 Action,通过第二个参数对象中的 dispatch 方法。这个方法和 getState 一样,也是 this 无关的。
- fetchList 中马上 updateCurrentPage,在请求返回时使用 getState 方法对 currentPage 判断,能够避免用户快速多次点击页码时发起多个 list 请求,请求返回的顺序不同可能导致问题。
- 异步 Action 没有更新应用状态的能力,想要更新应用状态必须 dispatch 同步 Action。下面的代码说明了为什么,感兴趣可以看看。
store.addAction('fetchList', function (page, {getState, dispatch}) {
dispatch('showLoading');
dispatch('updateCurrentPage', page);
return requestList(page).then(list => {
if (getState('currentPage') === page) {
dispatch('hideLoading');
// 如果异步 Action 支持在 promise 中返回 builder 并更新状态
// 这里的代码就可能导致问题。因为 promise.then 不是马上运行的
// 这里的 currentPage 不代表 builder 运行时的 currentPage
// currentPage 可能被另外一个 dispatch fetchList 改掉
// 所以这里应该 dispatch 一个同步的 Action 让应用状态即时完成变更
dispatch('updateList', list); // good
// return builder().set('list', list); // warning
}
});
});异步 Action 在 dispatch 时将返回 Promise 对象,以便于 Action 完成后的逻辑控制。
store.addAction('addArticle', function (article) {
return axios.post(url, article);
});
store.dispatch('addArticle', {}).then(() => {
// redirect to view page
});connect 方法支持对 默认store实例 和 San 组件进行连接,步骤和 redux 类似:
- 通过 connect 方法创建一个 connect 组件的函数
- 调用这个函数对组件进行 connect
import {store, connect} from 'san-store';
const connector = connect(
{name: 'user.name'},
{change: 'changeUserName'}
);
const UserNameEditor = san.defineComponent({/*...*/});
const NewUserNameEditor = connector(UserNameEditor);通常,我们只需要对当前声明的组件进行 connect。此时可以合并��一句
const UserNameEditor = san.defineComponent({/*...*/});
const NewUserNameEditor = connect(
{name: 'user.name'},
{change: 'changeUserName'}
)(UserNameEditor);当实际业务中需要多个 Store 实例时,可以自行创建 Store 实例。connect 方法支持连接到指定的 Store 实例。
import {Store, connect} from 'san-store';
// 自行创建 store 实例
const myStore = new Store({
initData: {
name:'erik'
},
actions:{
changeUserName(name) {
return builder().set('user.name', name);
}
}
});
const UserNameEditor = san.defineComponent({/*...*/});
// connect 时提供自创建的 storeA
const NewUserNameEditor = connect(
myStore,
{name: 'user.name'},
{change: 'changeUserName'}
)(UserNameEditor);mapStates 参数指定了要把哪些状态注入到组件,key 是要注入到组件的数据项名称,value 是 store 中状态项的名称。
import {store, connect} from 'san-store';
const NewUserNameEditor = connect(
{name: 'user.name'}
)(san.defineComponent({
// connect 后,name 数据项由 store 提供
template: '<div title="{{name}}">......</div>'
}));使用 store 时,我们可以通过调用 store.dispatch(actionName, payload) 方法更新应用状态。但如果在组件中也这么做,就会有些问题:
- 由于 actionName 的应用全局唯一性,名字需要比较完整,对于组件来说这么长的名称会显得比较冗余
- 组件实现时,得关心对具体 store 的依赖
通过指定 mapActions 可以在组件的 actions 成员上生成 dispatch action 的快捷方法,让组件可以更便捷的 dispatch action。mapActions 的 key 是要映射到组件 actions 成员上的方法名,value 是 action 的名称。
import {store, connect} from 'san-store';
const UserNameEditor = connect(
{name: 'user.name'},
{change: 'changeUserName'}
)(san.defineComponent({
submit() {
// 通过 mapActions,可以把 dispatch action 简化成组件自身的方法调用
// store.dispatch('changeUserName', this.data.get('name'));
this.actions.change(this.data.get('name'));
}
}));当实际业务中真的需要多个 Store 实例时,可以通过 connect 自行创建 connector,连接 Store 实例和 San 组件。步骤如下:
- 创建 Store 实例
- 通过 connect().connect() 方式,即 connect 的链式调用实现 连接多个 store
import {Store, connect} from 'san-store';
// 创建模块A中的store实例
const storeA = new Store({
initData: {
name:'erik'
},
actions:{
changeUserName(name) {
return builder().set('user.name', name);
}
}
});
const storeB = new Store({
initData: {
todos: []
},
actions:{
changeTodos(payload) {
return builder().set('todos', payload);
}
}
});
const Container = san.defineComponent({/*...*/});
// 调用手动创建的connectA方法进行storeA和组件连接
const NewContainer = connect(
storeA,
{name: 'user.name'},
{change: 'changeUserName'}
).connect(
storeB,
{todos: 'todos'},
['changeTodos']
)(Container);use api 提供了对 san-composition 形式组件的 store 支持:
- 使用
useState定义数据。 - 使用
useAction定义方法。
import san from 'san';
import {defineComponent, template, method} from 'san-composition';
import {useState} from 'san-store/use';
import {Store} from 'san-store';
// 创建模块A中的store实例
const myStore = new Store({
initData: {
name:'erik'
},
actions:{
changeUserName(name) {
return builder().set('user.name', name);
}
}
});
export default defineComponent(context => {
template(`
<div>{{name}}
<input value="{=newName=}"><button on-click="change">change</button>
</div>
`);
const name = useState(myStore, 'user.name', 'name');
const newName = data('newName', '');
let changeUserName = useAction(myStore, 'changeUserName');
method({
change: () => {
changeUserName(newName.get());
}
});
}, san);